 |
Главная |
Strain under acceleration 100 g and -100g
|
из
5.00
|
Because in such configuration of sensor momentum of rotation of proof mass is zero, when we consider only normal motion, the strain can be found from equation

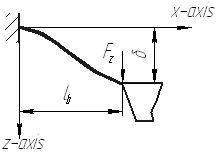
Figure 3. The shape of deflected beam.
From Fig. 3 it is clear that shape of deflected beam is symmetrical with respect to its central point. And the only difference is direction of curvature at edges of beam, and, subsequently, z position of polysilicon piazoresistor has different sign at different edges. So, the strains at 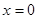 and
and 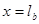 will just have different sign.
will just have different sign.
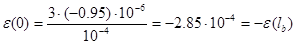
Where beam deflection 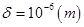 under acceleration 100g was found before. For opposite acceleration strains have opposite sign respectively.
under acceleration 100g was found before. For opposite acceleration strains have opposite sign respectively.
Because absolute value of strains for 100g and -100g are the same, further analysis will only due to acceleration 100g.
Sensitivity
Being under acceleration piezoresistors at different edges of beam will have opposite strains and will cause opposite addition to their own resistance. Taking also into account circuit of Wheatstone bridge we can calculate voltage difference 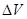 :
:



And relative changing of resistance can be obtained with the help of defined strain:
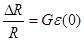
Applying that for polysilicon Gage factor is 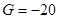

This is actually sensitivity under 100g acceleration. To obtain the sensitivity per unit acceleration we should do following:
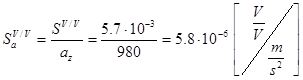
And for private case of input voltage  and acceleration
and acceleration  output is expected to be
output is expected to be
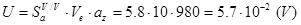
Thermal noise
Electric noise currents in circuit are caused by electrons thermal motion in wires. These currents will affect the minimum detectable acceleration (if we consider all other are ideal). And resolution of accelerometer due to thermal noise can be found as follows:
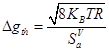
Where  is Boltzman constant, and
is Boltzman constant, and  is selected resistance of polysilicon piezoresistors, specific sensitivity
is selected resistance of polysilicon piezoresistors, specific sensitivity 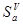 again is for operation mode
again is for operation mode  .
.

It was applied that sensor is operated at normal condition and 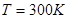 .
.
Resolution due to the ADC
As it was found in previous section, thermal noise is very small. So, another issue which should be considered in order to find resolution of our accelerometer is resolution due to used ADC. It is supposed that 16 but ADC will be used with designed sensor and it digitizes voltage in range -1.25V ~1.25V.

This error is much bigger and it will be dominant for accelerometer resolution.
Maximum acceleration
Polysilicon, which is piezoresistor’s material, can survive only if applied strain is less then 1%. If we use the same equation which was used to find strain four sections earlier we obtain the maximum allowable strain is equal to
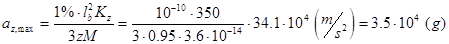
Found acceleration is very huge. But for 100g acceleration deflection is already of such magnitude, that small deflection assumption is hardly valid. For larger then 100g acceleration large deflection analysis must be used. At large deflection elongation of beams can’t be neglected and it will affect resulting strain. Therefore, maximum acceleration found above shouldn’t be considered as true value. But from earlier analysis we can conclude that designed sensor satisfies original spec to be able to measure acceleration in range -100g~100g.
|
из
5.00
|
Обсуждение в статье: Strain under acceleration 100 g and -100g |
|
Обсуждений еще не было, будьте первым... ↓↓↓ |

Почему 1285321 студент выбрали МегаОбучалку...
Система поиска информации
Мобильная версия сайта
Удобная навигация
Нет шокирующей рекламы

